-
Khanna Traders, are producer and supplier of scientific equipment.
- khannachahat05@gmail.com
-
+91-8930598097
-
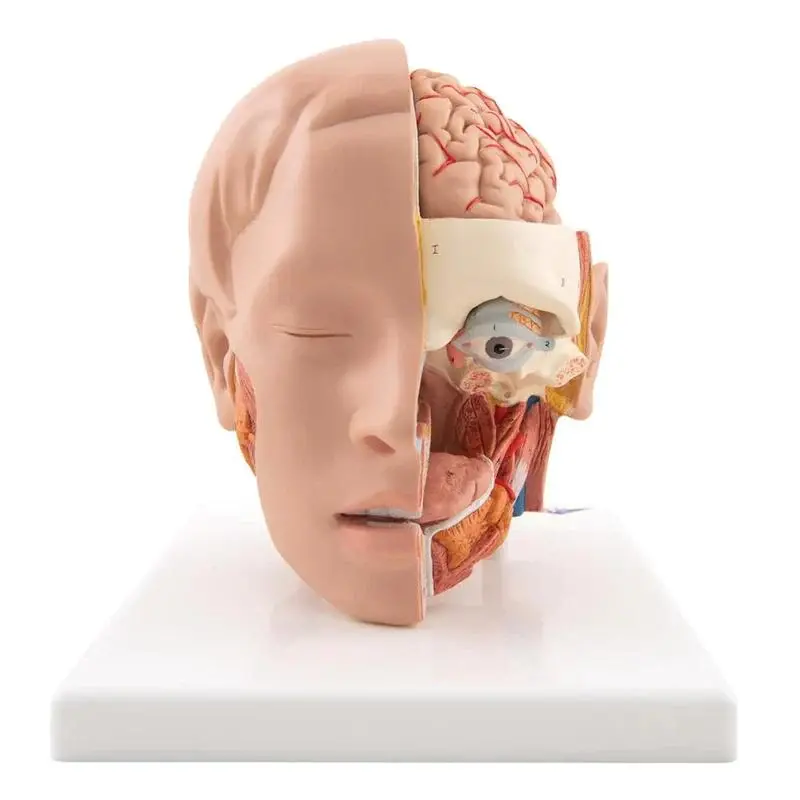 Anatomy Models
Anatomy Models
-
 Ayurveda Models
Ayurveda Models
-
- Panchakarma (Detoxification Therapies)
- Kaumarbhritya (Pediatrics)
- Prasuti Tantra & Stri Roga (Gynaecology & Obstetrics)
- Shalakya Tantra (ENT & Ophthalmology)
- Shalya Tantra (Surgery)
- Kayachikitsa (General Medicine)
- Swasthavritta (Preventive & Social Medicine)
- Agad Tantra (Toxicology & Forensic Medicine)
- Rognidan Evam Vikriti Vigyan (Pathology & Diagnosis)
- Rasa Shastra & Bhaishajya Kalpana (Ayurvedic Pharmacy & Alchemy)
- Kriya Sharir (Physiology)
- Rachana Sharir (Anatomy)
- Dravyaguna Vigyan (Ayurvedic Pharmacology & Medicinal Botany)
-
-
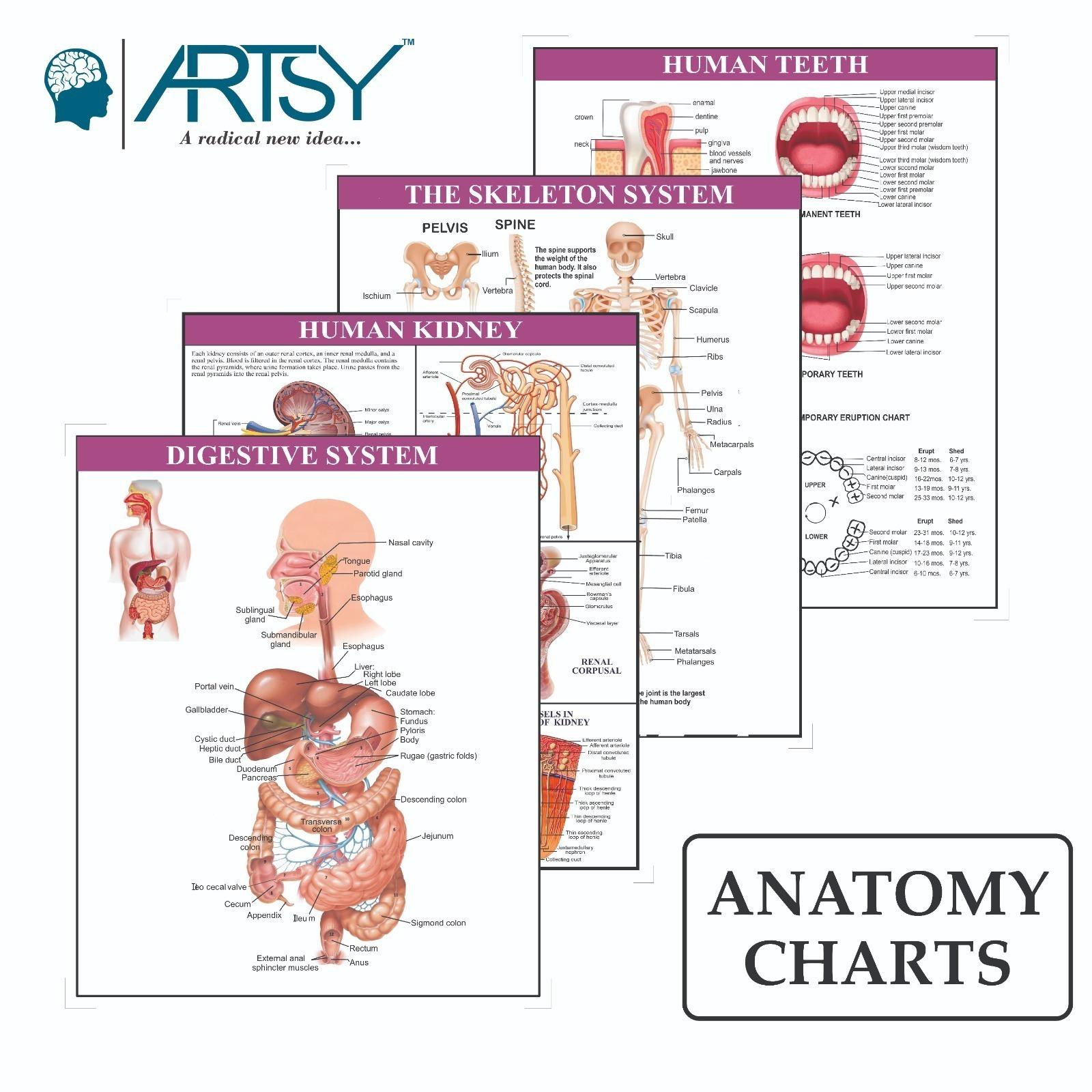 Charts
Charts
-
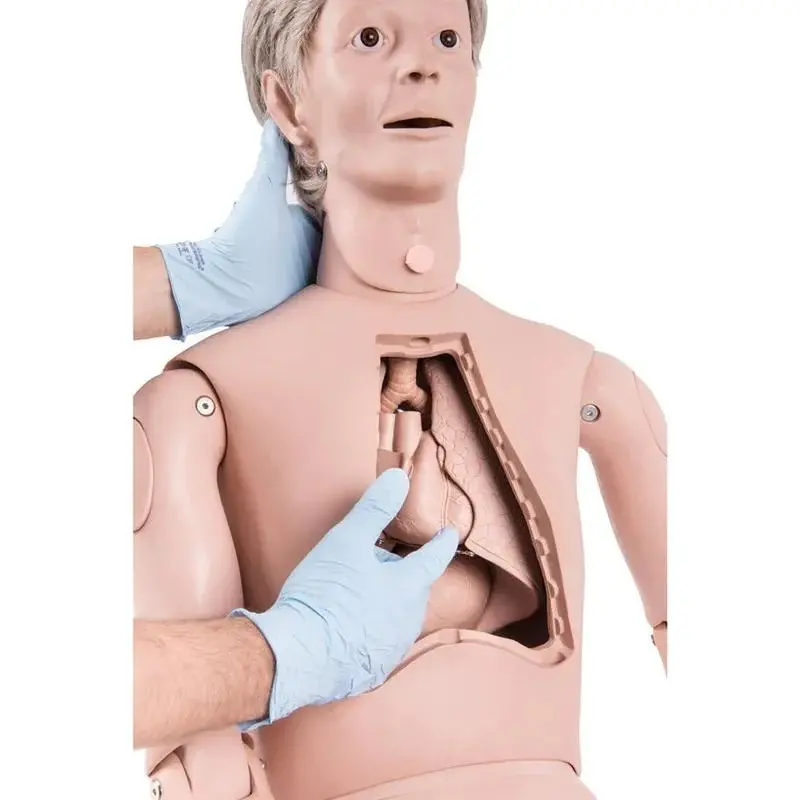 Medical Simulators
Medical Simulators
-
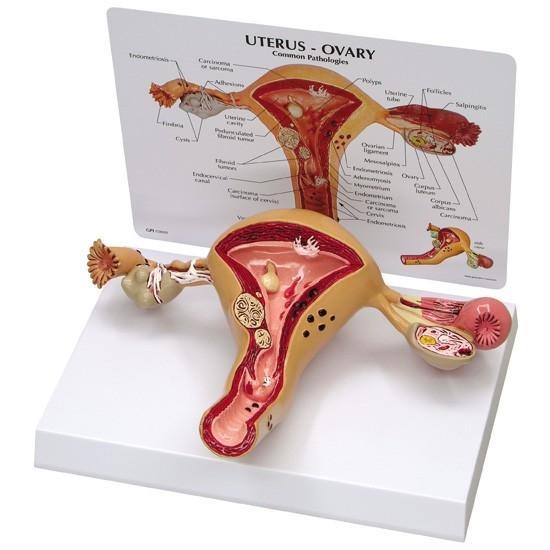 Women's Health Education
Women's Health Education
-
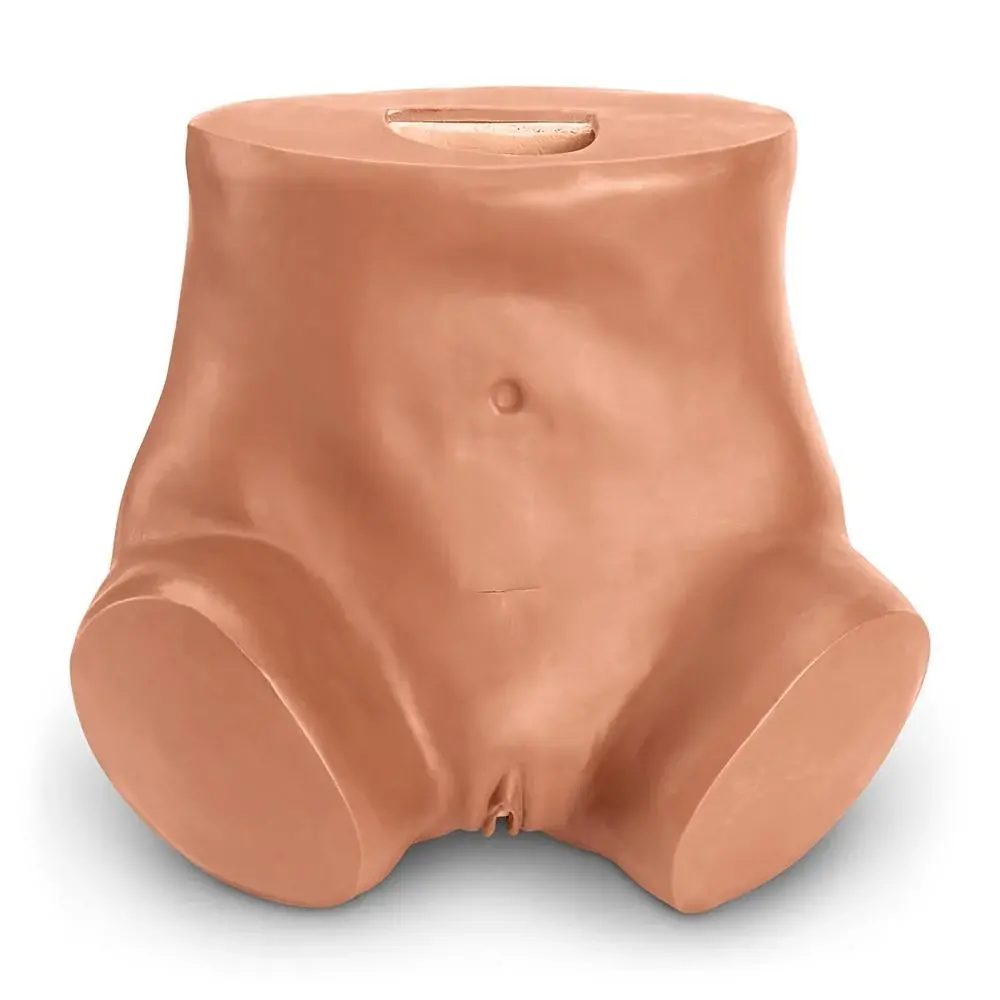 OB/GYN Trainers
OB/GYN Trainers
-
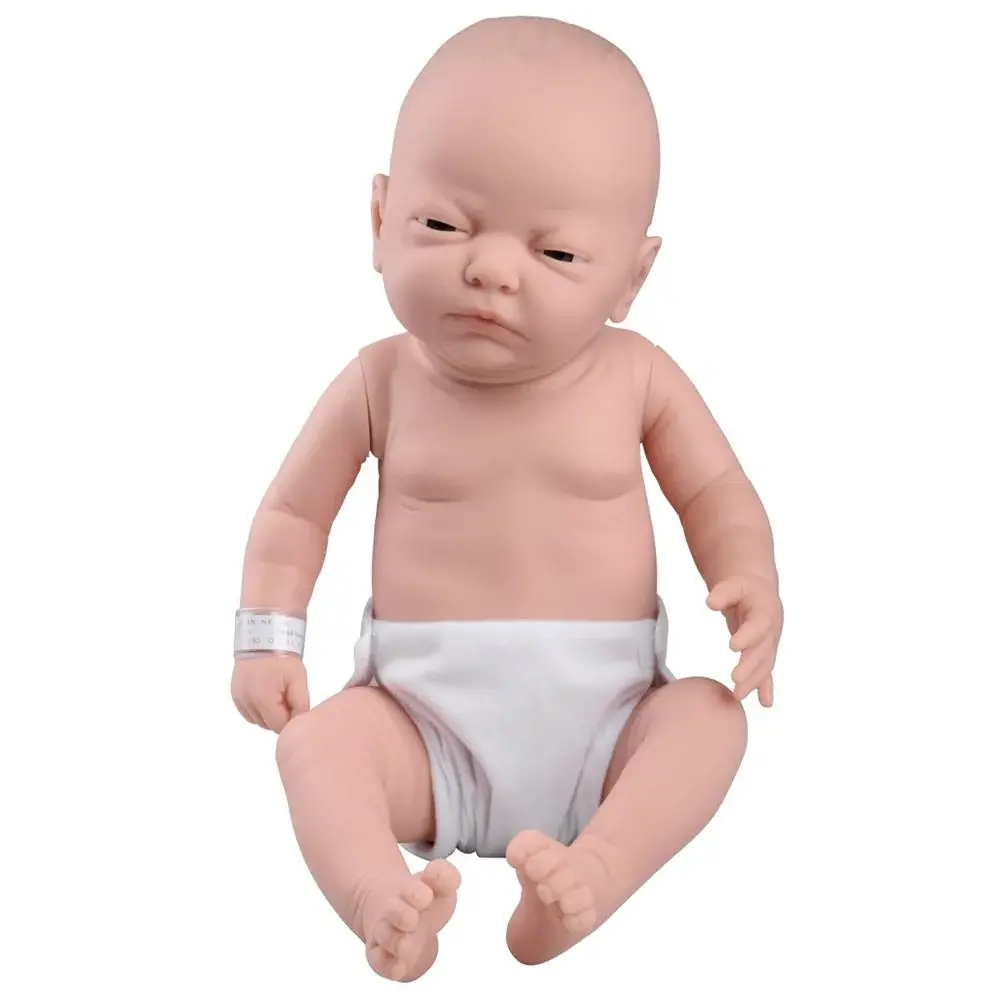 Baby Care Simulators
Baby Care Simulators
-
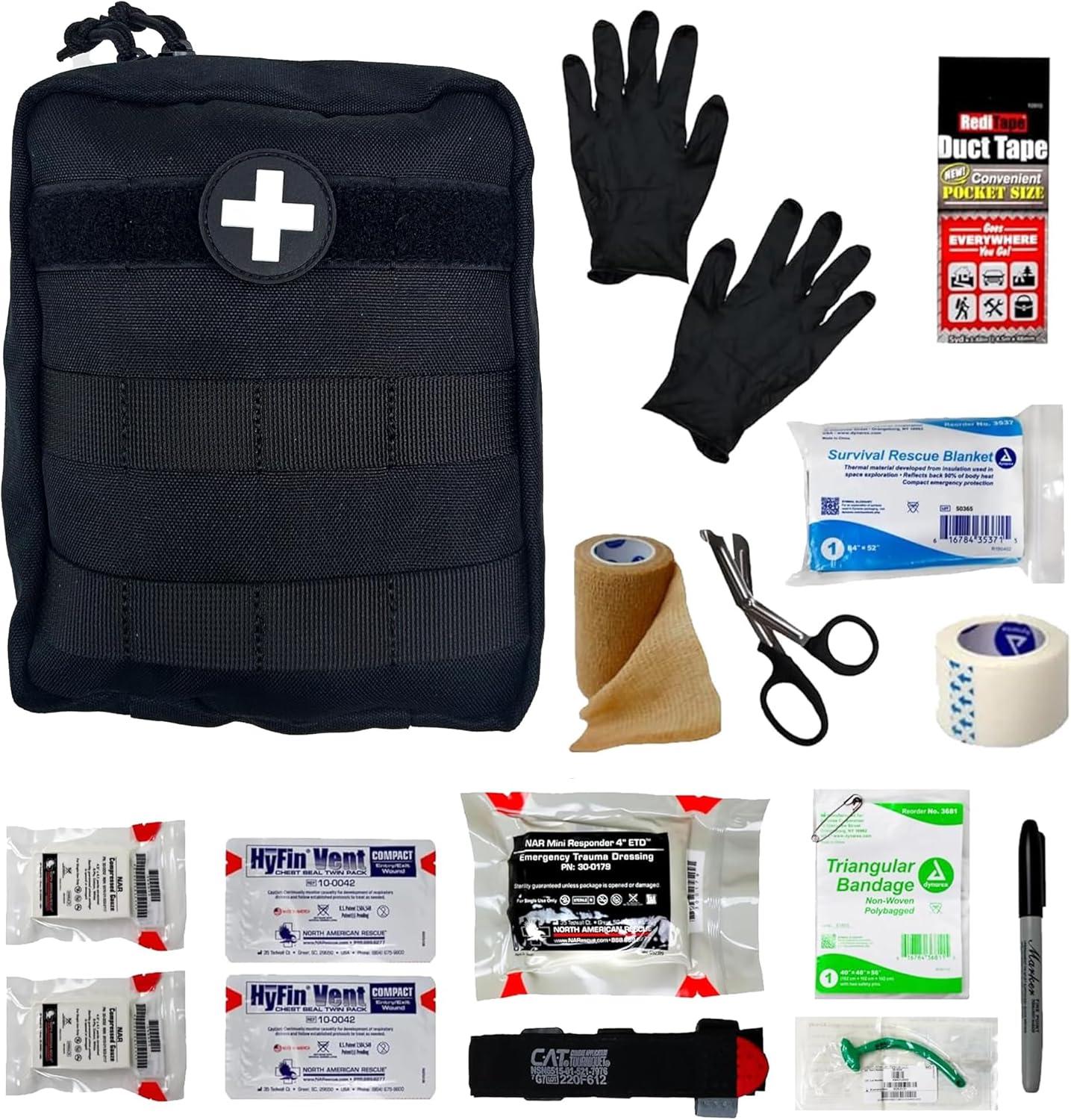 Medical/Emergency Rescue kit
Medical/Emergency Rescue kit
-
 BAMS Lab Setup
BAMS Lab Setup
-
- Rachana Sharir Department
- Kriya Sharir Department
- Dravyaguna Vigyan Department
- Rasa Shastra & Bhaishajya Kalpana Laboratory
- Swasthavritta & Yoga Laboratory
- Rog Nidan & Vikriti Vigyan Laboratory
- Panchakarma Laboratory
- Shalakya Tantra Laboratory
- Shalya Tantra Laboratory
- Agada Tantra, Vyavahara Ayurveda & Toxicology Laboratory
- Kaumarbhritya / Bala Roga Department & Laboratory
- Kayachikitsa Department & Laboratory
-
More Categories

